If you’re on the hunt for a groundbreaking technology that offers affordable, safe, and dependable long-range communication, you’re in the right place. Dive into the world of LoRaWAN this fresh wireless protocol is changing the game for IoT device interactions. We’ll delve into the essence of LoRaWAN, unravel its operating principles, and discover its diverse applications.
What is LoRaWAN?
LoRaWAN is a type of network known as a Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN), which is designed to connect and communicate over long distances while using very little power. It’s built on a method called LoRa modulation that allows smart devices, gateways, and users to talk to each other over distances of up to 15 kilometers- much farther than Wi-Fi can reach.
Plus, setting up a LoRaWAN network is usually cheaper than using cellular networks, especially in remote places. LoRaWAN meets all the key needs for Internet of Things (IoT) devices, like two-way communication, strong security from start to finish, the ability to move around without losing connection, and services that can pinpoint locations.
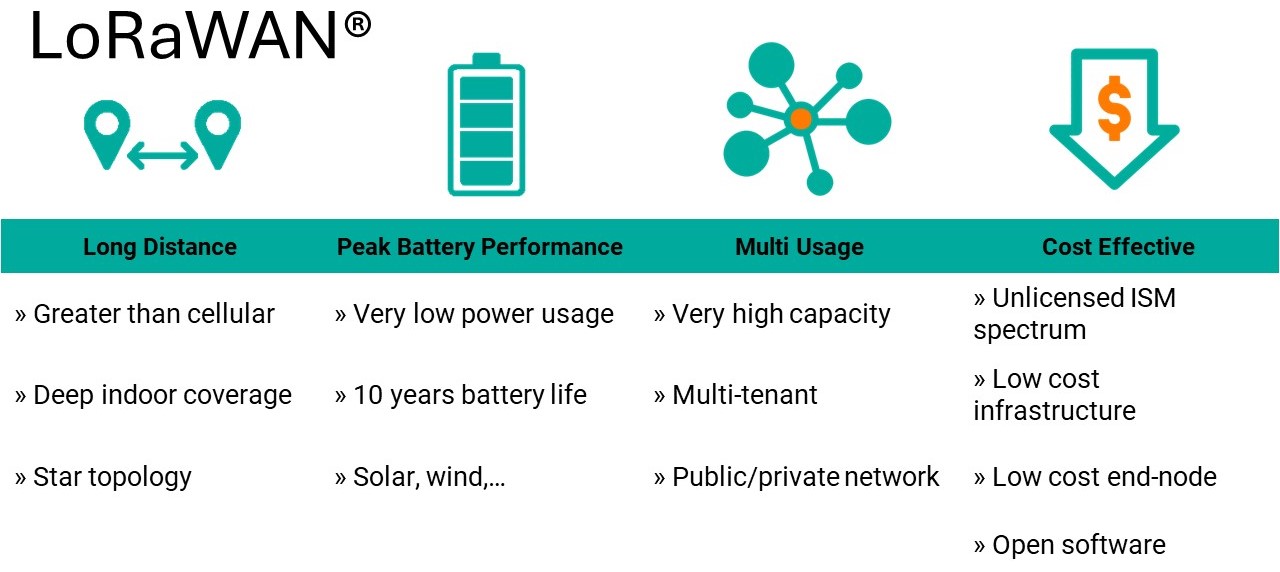
LoRaWAN is a technology that’s being used in many areas like smart buildings, farming, healthcare, and the oil and gas industry. The most popular uses of this technology today are:
- Metering: It’s used to measure how much water, gas, and electricity are being used.
- Tracking: It helps keep track of assets and people, how they’re being used, and keeps them safe.
- Managing Buildings and Property: It’s used in managing facilities and real estate.
- Industrial Uses: It’s used in various industries mainly to prevent problems before they happen, cut costs, and make things more efficient.
- Smart Cities: It’s used in many parts of smart cities, like controlling street lights, managing parking, collecting garbage, monitoring important infrastructure, and keeping an eye on the environment.
How LoRaWAN Connects Over Distance?
LoRaWAN is a special kind of network that’s built for sending messages over really long distances without using much battery power. It uses a special way of sending signals, called LoRa modulation, that lets things like sensors and gadgets talk to the internet without needing to be close by. They can be as far as 15 km away, which is a lot farther than Wi-Fi can go. It’s also not as expensive to set up as other ways to connect things over the internet, especially in places that are far from cities.
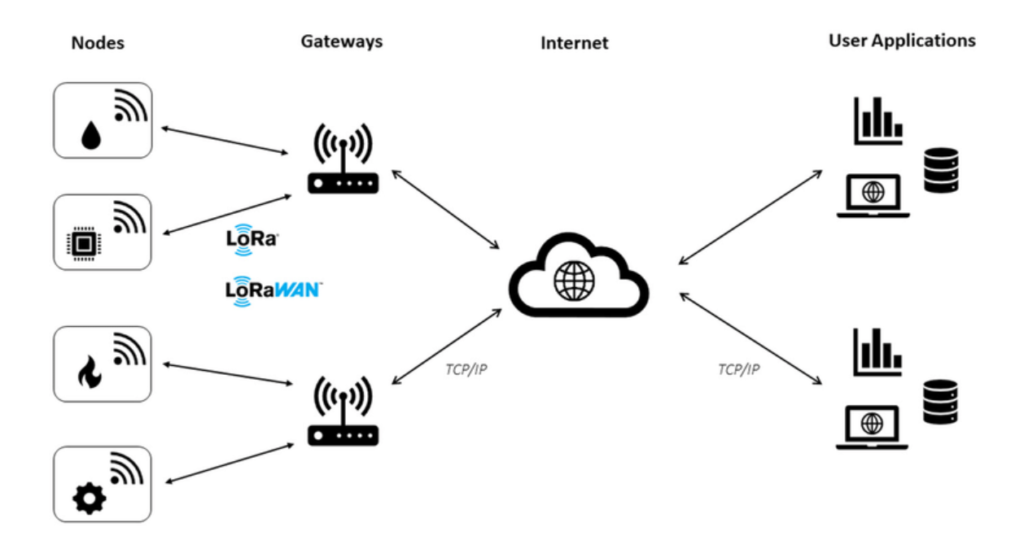
LoRaWAN is made to work well with IoT, which means it’s good at sending messages both ways, keeping data safe, letting devices move around, and figuring out where they are. It sends little packets of data over different radio frequencies, which means it can send information far and wide, quickly and without using a lot of power.
Definition of LoRaWAN gateways
Think of the LoRaWAN Gateway as a kind of post office for your smart devices. It covers a big area, just like a phone network does, and lets all your LoRaWAN gadgets send their messages to the internet and your apps. In simple terms, it’s the middleman that takes info from your devices and passes it on to the network server. The server then sorts this info and sends it where it needs to go. And it works both ways—your apps in the cloud can send messages back to your devices through the same route.
What are LoRaWAN Sensors?
LoRaWAN sensors are like little spies for the Internet of Things (IoT). They use LoRaWAN to chat with a central system, sending back all sorts of information. They’re great for keeping an eye on things that are far away—like tracking where stuff is, checking the weather, or gathering different kinds of data. They don’t need much power to work and can send signals over really long distances. Plus, they’re smart enough to adjust how they send data, so whether they’re close by or far off, they do it in the most efficient way possible.
LoRa, LoRaWAN, and LPWAN
LoRa, LoRaWAN, and LPWAN are types of tech that help devices connect over the Internet of Things (IoT), which is like a big web of connected gadgets. They’re really good at sending data far without using much battery or costing a lot. Even though LoRaWAN and LPWAN are pretty similar, they each have their own special features, like how fast they send data and how far they can reach.
LoRa®
Imagine LoRa as a way for devices to whisper to each other from miles away without shouting. It’s a tech that lets them send data really far while keeping their energy use low. It’s perfect for when you need to check on things that are far apart, like keeping track of trucks or machines talking to each other.
LoRaWAN®
Now, LoRaWAN is like a big network that uses LoRa to let devices talk securely and reliably. It’s like having a bunch of walkie-talkies that all connect through a few main stations, making sure messages get to the internet safely and without costing too much. It’s great for all sorts of IoT stuff, from smart farming to finding lost pets.
LPWAN
LPWAN, or Low Power Wide Area Network, is a type of wireless network. It’s built to use less energy and cover large areas. It’s perfect for things like sensor networks that don’t need to send a lot of data quickly. While LoRa is one technology that can be used for LPWAN, it’s not the only one. There are others like Sigfox, NB-IoT, and Weightless. So, think of LPWAN as a big, energy-saving network that’s great for small amounts of data over long distances.
LORAWAN CLASSES
LoRaWAN has three types of devices, each with different abilities and power usage: Class A, Class B, and Class C.
Class A devices are the most power-efficient. They’re battery-powered and can last for years. This is because they’re only active for a short time when they send their data and for a brief period afterward to allow the network to talk to them. The rest of the time, they’re in a power-saving sleep mode. They use a communication design that allows them to start communication whenever they want and includes two short receive windows after they send data. This is great for applications that need a quick response after sending data.
Class B devices are an upgrade from Class A. They can schedule times to receive data from the network. This lets applications send control messages without waiting for the device to send data first. But before they can receive these messages, Class B devices need to sync their timing with the network. Once they’re synced, they go into receive mode during their scheduled times to make sure they can get any data the network sends. This means Class B devices respond faster than Class A devices, but they use more battery power than Class A and less than Class C.
Class C devices can communicate with the network almost anytime. They use more power than Class A or B devices, but they have the fastest response time when sending data from the application to the device.
Different choices to LoRaWAN
While LoRaWAN is a common choice for networks that need to cover large areas and use little power (LPWANs), there are other options like Sigfox, Weightless, and NB-IoT.
Sigfox is a technology that lets devices communicate over long distances while using little power. It works in the ISM band, which is unlicensed, so it’s cheaper and easier to set up. But Sigfox relies on one vendor, unlike LoRaWAN, which has a large and diverse group of supporters. Also, Sigfox’s two-way communication is limited.
Weightless P is another LPWAN technology. It uses radio waves to send data over long distances while using little power. It’s good for applications that need cheap, low-power connectivity, but it has limited capacity and its infrastructure is costly. Again, LoRaWAN offers more choices in equipment.
NB-IoT is designed for low-power, cheap, long-distance communication. It’s better for applications that need to send more data than other LPWAN technologies. It’s a cellular-based LPWAN technology, so it has wide coverage, but each device needs a sim card/data plan, which can be costly.
We should also talk about Wi-Fi and cellular networks. Wi-Fi is a local network technology that’s often used to provide internet access in homes, businesses, and public places. It’s widely available and is usually the first choice for internet access. But it can’t cover large areas and needs many routers to do so.
Cellular networks are mobile networks that use radio waves to send and receive data. They’re usually used to provide internet access to mobile devices like smartphones and tablets. Cellular networks are more reliable and faster than Wi-Fi and can provide internet access in more remote areas. But they’re more expensive to set up and maintain, and each device needs its own data plan.
Advantages of LoRaWAN
LoRaWAN has a big impact on the battery life of the device, the capacity of the network, the quality of service, security, and a variety of programs that serve the network.
Smart Energy Consumption A LoRaWAN device only sends information when it has data ready to send. This is known as the Aloha method. In contrast, in a cellular network or a synchronous network, devices often have to “wake up” to sync with the network and check messages. This synchronization uses a lot of power and is the main reason for reducing battery life.
Network Capacity Many networks use a “mesh” network structure. In a mesh LPWAN network, each device forwards the information of other devices to increase the communication range and cell size of the network. While this increases range, it also adds complexity, reduces capacity, and reduces battery life because devices forward and receive irrelevant information from other devices. That’s why the long-range star structure of LoRaWAN is the best choice for preserving the battery life of the device when long-range connectivity can be achieved.
Quality and Security of Service In LoRaWAN, devices are not connected to a specific gateway. Instead, data sent by a device is usually received by multiple gateways and forwarded to the central network server where the messages are checked and securely forwarded to its application.
The intelligence and complexity are transferred to the network servers that manage the network. They will filter out redundant packets received, perform security checks, schedule acknowledgments through the optimal gateway, perform adaptive data rates, and more. If the device is mobile or moving, there is no need to pass control from gateway to gateway, which is a key feature that allows the asset tracking application.
LoRaWAN Specifications
The details of LoRaWAN can change depending on the region and the specific rules of the country where it’s being used.
LoRaWAN in Europe In Europe, LoRaWAN uses a regional channel plan based on the 863-870 MHz range. You can use this frequency band without a license as long as you keep the transmit power at 14 dBm and don’t transmit more than 1% of the time.
LoRaWAN in North America In North America, the ISM band is 902-928 MHz. LoRaWAN uses 64 channels that are 125 kHz wide, ranging from 902.3 MHz to 914.9 MHz, plus 8 channels that are 500 kHz wide, ranging from 903 MHz to 914.2 MHz for sending data. For receiving data, the channels are also 500 kHz wide and range from 923 MHz to 928 MHz.
In North America, the maximum transmit power is less than 30 dBm if you’re using a frequency hopping device over more than 50 channels. If you’re hopping over fewer channels, you can operate at a lower power level, 20 dBm. According to the FCC, there’s no limit on how much you can transmit, but each message can’t be longer than 400 milliseconds.
Is LoRaWAN secure?
Yes, it is. LoRaWAN uses a type of encryption called AES-128 to keep data safe from being messed with or intercepted. It uses something called a Network Session Key to make sure every message from verified devices is correct and hasn’t been tampered with. It also uses an Application Session Key to keep messages private all the way to their final destination. Lastly, all communications go through a special network server, which adds another layer of security. So, in short, LoRaWAN takes several steps to ensure the security of its network.
Restrictions of LoRaWAN
While LoRaWAN has many benefits, there are some things to keep in mind before you decide to use it.
Firstly, LoRaWAN doesn’t cover everywhere. Unlike cell networks, you might want to use LoRaWAN in a place that doesn’t have network coverage. Luckily, you can work with LoRaWAN network operators to extend their coverage to your area, or you can set up and run your own network.
Secondly, if you’re using mobile devices, you’ll need coverage across all the areas your devices will move through. This might mean setting up roaming agreements with network operators nearby. It’s likely your devices will move across a larger area than the network you’re interested in running, so working with other networks can be very helpful.
Thirdly, LoRaWAN has a limited data rate, less than 50 kbps. This means it’s not suitable for applications that need to send a lot of data quickly, like streaming video or audio.
Is it fast? Well, LoRaWAN isn’t particularly fast, but it’s designed for low-power, long-range communication that doesn’t need to send a lot of data. Data rates can range from 0.3 kbps up to 50 kbps, and it can cover a long range of up to 15km (10 miles). So, if you need to send measurements and reports, it’s fast enough, but it won’t be a good choice for sending videos or images.
But if you keep these limitations in mind when deciding whether to use LoRaWAN, and most importantly, think about what you need it for, you’ll be able to take full advantage of all the benefits LoRaWAN has to offer.
Short summary
LoRaWAN is a network that can function where others can’t, due to issues like long distances, high power use, heavy traffic, or lack of coverage. In places where it’s not possible to install cables, a LoRaWAN antenna can step in. This standard is made to connect devices that need to send small amounts of data over long distances, and it uses very little power, which can help lower the cost of sensors.
The openness of the standard, the durability of the network equipment, the high energy efficiency, the lack of regulatory hurdles, and the flexibility of the solutions make LoRaWAN a nearly perfect standard for the Internet of Things.
So, if you’re looking for a dependable network for your IoT infrastructure or devices to create a smart environment, LoRaWAN is definitely worth considering.

