While everyone is talking about Wi-Fi 7 because it’s the latest and quickest Wi-Fi available, there’s another wireless technology named Wi-Fi HaLow that’s slowly but surely making a big impact on the world of Internet of Things (IoT). Here’s all the important information about Wi-Fi HaLow.
Wi-Fi HaLow: What is this?
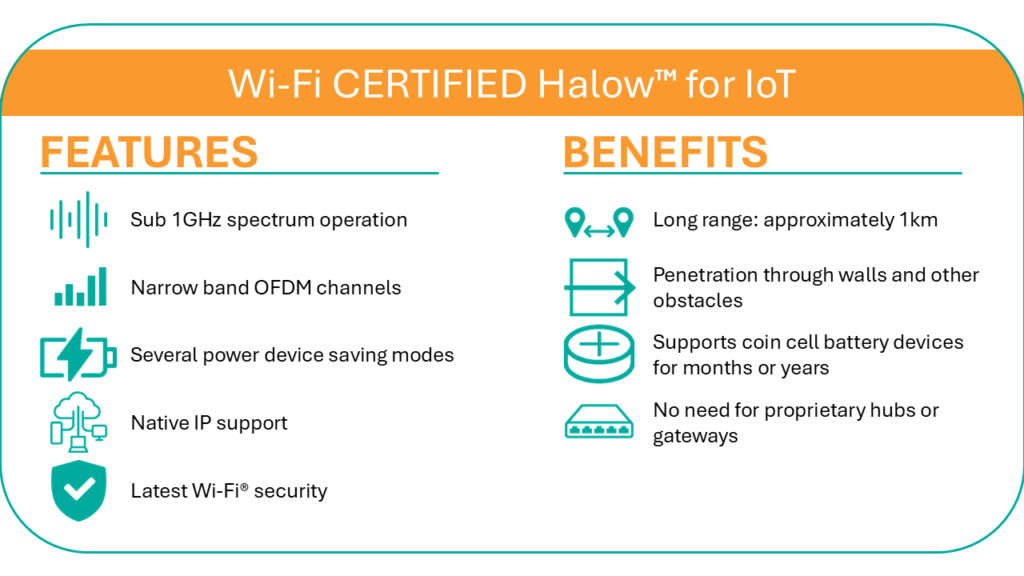
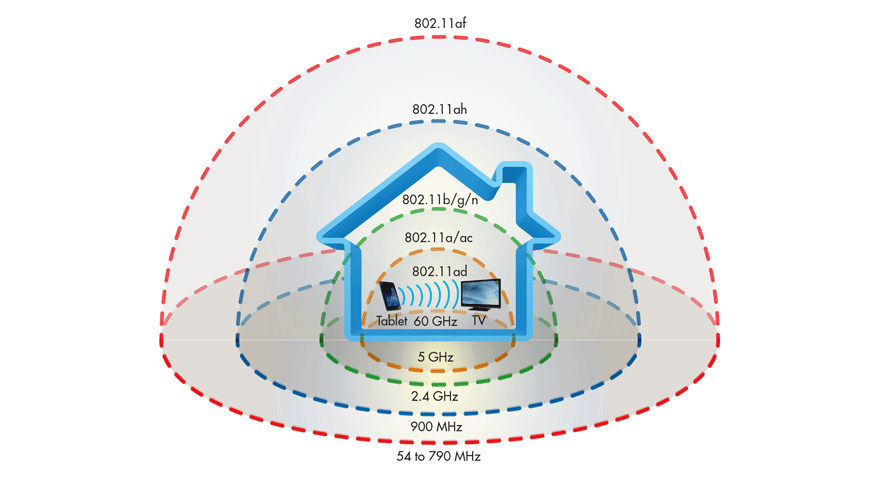
Wi-Fi HaLow is a type of wireless technology that follows the IEEE 802.11ah rules. It was first brought to the public in 2016. What makes it different from the usual Wi-Fi 5, Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 6E, and Wi-Fi 7 is that it operates on frequencies below 1GHz. On the other hand, the traditional Wi-Fi versions use frequencies of 2.4GHz, 5GHz, and 6GHz.
Wi-Fi HaLow uses lower frequencies which can go further, so it can connect devices up to a kilometer away, or even more if there’s nothing blocking the signal. But, because it uses a lower frequency, it has smaller channels and less bandwidth, which means it can’t transfer data as quickly. However, it can still provide speeds from 150Kbps over long distances to 86.7Mbps over short distances.
Wi-Fi HaLow isn’t meant to replace the Wi-Fi we’re used to. It’s actually designed to work alongside the existing Wi-Fi standards to provide connections over longer distances without the need for extra equipment like wireless extenders, multiple access points, or complicated wired setups. It’s particularly useful for Internet of Things (IoT) devices, projects in smart cities, and mesh networks.
In the US, Wi-Fi HaLow uses the 900Hz frequency, which is part of the spectrum that doesn’t require a license, so it’s free for everyone to use. But in other countries, Wi-Fi HaLow might use different frequencies, depending on which ones below 1GHz are available.
How Does Wi-Fi HaLow Differ From Regular Wi-Fi?
While the usual Wi-Fi protocols have greatly improved in terms of wireless speeds and response times, their signal range hasn’t kept up. Wi-Fi HaLow is designed to address this issue, especially in a world where the number of Internet of Things (IoT) devices is rapidly increasing and these devices need a dependable way to stay connected to each other and the internet.
Wi-Fi HaLow can transmit signals much further than regular Wi-Fi. More importantly, because it uses a lower frequency, it’s better at getting through obstacles like walls. This is similar to how 2.4GHz Wi-Fi has a better signal range and can penetrate walls better than 5GHz and 6GHz Wi-Fi.
Wi-Fi HaLow also uses less power, as it can go into a very low power state thanks to various sleep modes defined in the 802.11ah rules. This makes it ideal for devices that run on batteries, like sensors and wireless security cameras. These devices can operate for months or even years without needing a new battery or a recharge.
Another benefit of Wi-Fi HaLow over regular Wi-Fi is that it can connect with more than 8,000 devices at the same time, compared to 2007 devices for Wi-Fi 6.
How Do Z-Wave, Zigbee, or Thread Compare?
Wi-Fi HaLow isn’t the only wireless technology that’s designed to connect IoT devices. There are others, like Z-Wave, Zigbee, and Thread, each with their own strengths and weaknesses.
Z-Wave has a lot in common with Wi-Fi HaLow. It also operates on frequencies below 1GHz, which gives it a good range and low power usage. However, even though it can transmit signals a long way, it can’t go as far as HaLow. Also, a single Z-Wave network can only support up to 232 devices. And to use Z-Wave devices effectively, you need a special controller.
It’s worth noting that in 2020, the Z-Wave Alliance introduced a new version called Z-Wave Long Range. This version can transmit signals as far as Wi-Fi HaLow and can support up to 4,000 devices on a single network.
Wi-Fi HaLow isn’t the only wireless technology made for connecting IoT devices. There are others like Z-Wave, Zigbee, and Thread, and each has its own pros and cons.
Z-Wave shares some similarities with Wi-Fi HaLow. It also uses frequencies below 1GHz, which allows it to have a good range and use less power. But, while it can send signals quite far, it can’t reach as far as HaLow. Also, a single Z-Wave network can only support up to 232 devices. And to make Z-Wave devices work well, you need a specific controller.
It’s interesting to note that in 2020, the Z-Wave Alliance introduced a new version called Z-Wave Long Range. This version can send signals as far as Wi-Fi HaLow and can support up to 4,000 devices on a single network.
So, while each of these low-power wireless protocols does a lot of things well, they each have their own limitations. In contrast, Wi-Fi HaLow has a great signal range, doesn’t require a hub, has strong security, can connect to over 8,000 devices, and has decent data transmission speeds. Plus, it works seamlessly with other devices, and because it uses a different frequency band than existing Wi-Fi networks, HaLow doesn’t interfere with the existing setup.
What Are the Advantages of Wi-Fi HaLow for You?
Wi-Fi HaLow can be useful in many situations, but it’s likely to have the biggest impact on regular home users, especially those with smart home devices, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and mesh networking systems. As more and more household devices become smart and need wireless access, the 2.4GHz wireless band is getting crowded because it can only have three channels that don’t overlap.
But Wi-Fi HaLow works on a completely different frequency than regular Wi-Fi and can have over 26 channels that don’t overlap. This means there’s almost no chance of interference or congestion unless you have a huge number of devices trying to connect at the same time.
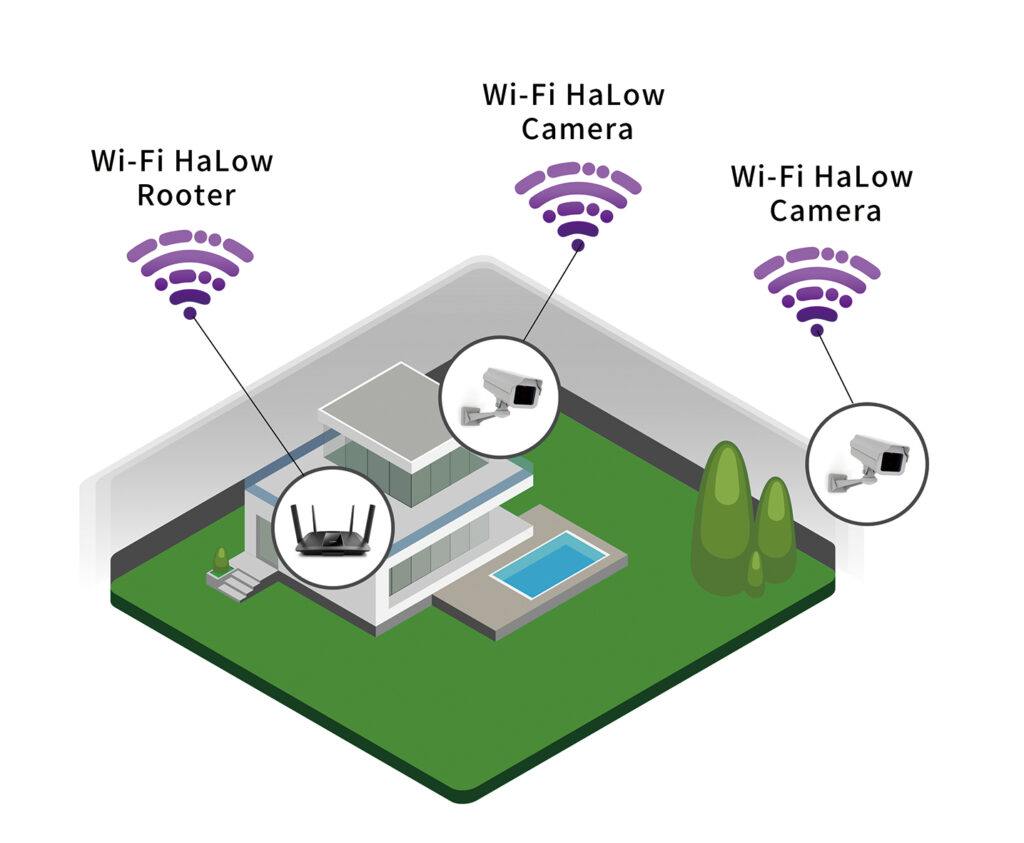
What’s more, Wi-Fi HaLow’s long range means it can connect IoT and smart home devices across large properties from just one access point. So, for instance, you could have a single router or a mesh system covering your main house for devices that need a lot of bandwidth.
But if you add Wi-Fi HaLow to the mix, the same router or mesh system can also cover sensors, security cameras, and other devices that don’t use much bandwidth on the edges of your property, in outbuildings, guest houses, and other parts of your property. This means you don’t need to wire up your whole property or install extra mesh nodes or Wi-Fi extenders to get a good signal everywhere.
What Are the Steps to Acquire Wi-Fi HaLow?
Just like with any new Wi-Fi technology, both your wireless router and your device need to support Wi-Fi HaLow for you to take advantage of it. Sadly, not many devices support Wi-Fi HaLow yet, but as more people become interested in it, we should start to see more devices that do.
Some companies have already started to release Wi-Fi extenders that use HaLow, which can extend the range of a wireless network to hundreds of meters. As for devices, a company called Abode unveiled a new security camera named Edge at CES 2024 that uses Wi-Fi HaLow. It’s expected to be available for purchase in the first quarter of 2024 for around $200. A Taiwanese company called Chicony is also planning to release security cameras that use Wi-Fi HaLow.
Unfortunately, you can’t just update the firmware of your existing wireless router or device to get the benefits of HaLow. It needs new hardware. This is the same as how you can’t get access to Wi-Fi 7 by updating the software on a Wi-Fi 6E router or device.
A Dependable, Albeit Slower, Wi-Fi Pathway for IoT
Wi-Fi HaLow completes the Wi-Fi connectivity freeway by essentially adding a slow lane for Internet of Things devices that is reliable, secure, and seamless. This way, the existing connectivity freeway remains undisturbed, and moving IoT devices from existing lanes to the slow lanes also clears up bandwidth for other devices.
Read more:

